An Overview of the Model Organism: C. Elegans
6/3/2014
JoVE Science Education Database. Model Organisms I: yeast, Drosophila and C. elegans. An Overview of the Model Organism: C. elegans. Journal of Visualized Experiments, Cambridge, MA, doi: 10.3791/5103 (2014).
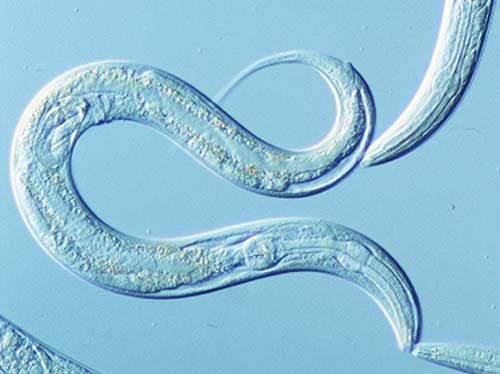
Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic, soil-dwelling roundworm that has been powerfully used as a model organism since the early 1970″s. It was initially proposed as a model for developmental biology because of its invariant body plan, ease of genetic manipulation and low cost of maintenance. Since then C. elegans has rapidly grown in popularity and is now utilized in numerous research endeavors, from studying the forces at work during locomotion to studies of neural circuitry. This video provides an overview of basic C. elegans biology, a timeline of the many milestones in its short but storied history, and finally a few exciting applications using C. elegans as a model organism.
C. elegans Maintenance
Ceanorhabditis elegans has been, and is still, used to great success as a model organism for studying a variety of developmental, genetic, molecular and even physical phenomena. In order to use C. elegans to its full potential, proper care and attention to the basic maintenance of this powerful organism is essential.
In this video you will learn the basic housing and feeding requirements of C. elegans, how to correctly handle and manipulate worms using a worm pick and how to freeze and recover important worm stocks. Towards the end of the video we will visit a few applications of modifying the housing, feeding and manipulation of these important animals.
Caenorhabditis elegans Development and Reproduction
Ceanorhabditis elegans is a powerful tool to help understand how organisms develop from a single cell into a vast interconnected array of functioning tissues. Early work in C. elegans traced the complete cell lineage and structure at the electron microscopy level, allowing researchers unprecedented insight into the connection between genes, development and disease. Appreciating the stereotyped development and reproductive program of C. elegans is essential to using this model organism to its experimental fullest. This video will give you a peek into the development of a worm from fertilization to hatching, and walk you though the life stages of the newly hatched larvae on its journey to reproductive maturity. The video will detail how the major axes are established, which founder cells give rise to what tissues in the developing embryo and how to discriminate between the four larval stages. Finally, you will learn how to set up a genetic cross and we”ll visit a few applications that manipulate the development and reproduction of C. elegans to experimental benefit.
RNAi in C. elegans
RNA interference (RNAi) is a widely used technique in which double stranded RNA is exogenously introduced into an organism, causing knockdown of a target gene. In the nematode, C. elegans, RNAi is particularly easy and effective because it can be delivered simply by feeding the worms bacteria that express double stranded RNA (dsRNA) that is complementary to a gene of interest. First, this video will introduce the concept of RNA interference and explain how it causes targeted gene knockdown. Then, we will demonstrate a protocol for using RNAi in C. elegans, which includes preparation of the bacteria and RNAi worm plates, culturing of the worms, and how to assess the effects of RNAi on the worms. RNAi is frequently used to perform reverse genetic screens in order to reveal which genes are important to carry out specific biological processes. Furthermore, automated reverse genetic screens allow for the efficient knockdown and analysis of a large collection of genes. Lastly, RNAi is often used to study the development of C. elegans. Since its discovery, scientists have used RNAi to make tremendous progress on the understanding of many biological phenomena.
C. elegans Chemotaxis Assay
Chemotaxis is a process in which cells or organisms move in response to a chemical stimulus. In nature, chemotaxis is important for organisms to sense and move toward food sources and move away from stimuli that may be toxic or harmful. Chemotaxis is also important at the cellular level. For example, chemotaxis is required for the movement of sperm toward an egg prior to fertilization. In the lab, chemotaxis is frequently examined in the nematode, C. elegans, which is known to migrate towards food sources in soil, but away from toxins such as heavy metals, substances with a low pH, and detergents. This video demonstrates how to perform a chemotaxis assay, which includes preparing the chemotaxis plates and the worms, running the assay, and analyzing the data. Then, we discuss examples of how chemotaxis assays can be used in C. elegans as a tool to understand learning and memory, olfactory adaptation, and neurological disease such as Alzheimer”s disease. Chemotaxis experiments in C. elegans have near-limitless possibilities for learning more about the cellular and genetic mechanisms of many biological processes, and may lead to a greater understanding of human biology, development, and disease.
 Immune & Epithelial Interactions
Immune & Epithelial Interactions